Training isn’t one-size-fits-all—especially when you’re building programs for different roles, goals, and business challenges.
At Arlo we work with in-houses training team, and instructional designers who are in-charge of identifying and implementing employee training programs, and there are a tonne of different internal training types that can fall under this bracket, from leadership development programs through to cybersecurity.
We’ve compiled this guide to the most common types of employee training programs we’ve heard about, from our own internal training processes, or our customers.
We’ve included some points for each on what makes each type of program effective, and some of the core components each type of program should includes.
But before jumping into the example’s let’s take a quick look at some of the general benefits of employee training 👇
Benefits of Employee Training
1. Builds a Future-Ready Workforce
Training is an investment in your company’s future. By equipping employees with skills and knowledge you’re preparing them to take on tomorrow’s challenges with confidence.
And in turn help employee productivity, according to Gallup companies are 17% more productive when employees get the training they need.
2. Boosts Confidence and Competence
When people know what they’re doing, they do it better. Quality training programs give employees the tools and clarity they need to make smart decisions, take ownership of their roles, and perform at a higher level.
LinkedIn’s 2024 Workplace Learning Report, notes that 8 in 10 people say learning provides them with a sense of purpose at work, and 7 in 10 says learning improves their connection with their company.
3. Improves Bottom Line
Strategic training initiatives have a direct, measurable impact on business performance. 43% of companies report increased revenue after implementing an education program.
The structure of the program matters. 60% of companies with curriculum-based education initiatives reported revenue growth.
In addition to top-line growth, training programs can reduce operational costs. 27% of companies have seen a decrease in support costs after implementing education programs, thanks to improved employee knowledge and fewer process errors.
1. Customer Service Training
Customer service training goes far beyond “being nice to customers.”
It’s about equipping frontline teams with the skills, context, and confidence to handle complex interactions—especially under pressure.
It becomes especially critical when launching a new product, onboarding new service staff, addressing rising complaint volumes, or after identifying service gaps through customer feedback or CSAT scores.
In the image below, you can see an example of a training provider ‘Dale Carnegie’ who run customer service training programs for companies. Many companies seek out an external provider who have expert trainers available that can come in and help their team upskill.
Customer Service Training Program Example
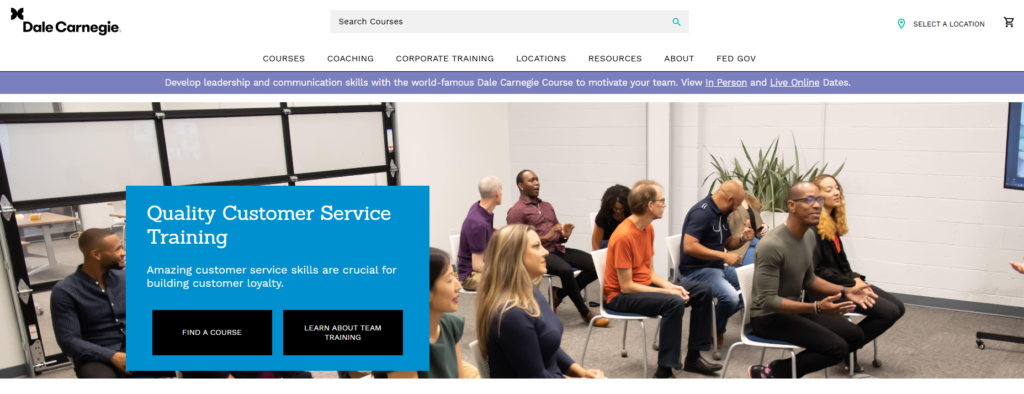
Effective Customer Service Training Should:
Work on Crucial Soft Skills: Training should focus on developing interpersonal abilities essential for positive interactions.
This includes active listening to truly understand customer needs, demonstrating empathy to connect with their perspective, and mastering conflict de-escalation techniques to professionally manage difficult situations and maintain rapport.
Deepen Product or Service Knowledge: Effective customer service training means employees have a comprehensive understanding of the company’s offerings.
Empowering to answer customer questions accurately, provide relevant recommendations confidently, troubleshoot issues efficiently, and ultimately build customer trust through knowledgeable support.
Develop Situational Problem-Solving Abilities: Equip employees with the skills and confidence to navigate challenging customer service scenarios effectively.
Training should cover practical strategies for handling difficult or upset customers, managing expectations realistically to prevent disappointment, and resolving issues promptly and appropriately at the first point of contact whenever possible, minimizing the need for escalation.
Strong Customer Service Training Program Typically Includes These Key Components:
- Core Communication Skills Modules: Focusses sessions on active listening techniques, demonstrating empathy verbally and non-verbally, using positive language, and managing an appropriate tone.
- Product/Service Deep Dives: Training on the features, benefits, use cases and technical aspects of the company’s offerings.
- Conflict Resolution & De-escalation Workshops: Practical training with techniques and frameworks for managing angry or upset customers, calming tense situations, and finding agreeable solutions.
- Scenario-Based Learning & Role-Playing: Opportunities for employees to practice handling realistic customer interactions (e.g., complaints, complex queries, technical issues) in a simulated environment with feedback.
- Training on Support Systems & Tools: Instruction on effectively using essential tools like the CRM system, ticketing software, knowledge base, and communication platforms.
2. Compliance Training
Compliance training makes sure all employees follow the laws, policies, and standards that affect their roles.
The purpose is of course to protect the company legally, but also to create an environment where employees are in a position where they can make the right decisions, and are empowered to do so.
Compliance Training Program Example
In the example below, you can see a compliance program offered by Arlo customer, the Winnipeg Construction Association. The program is aimed at helping construction professionals in Manitoba, remain compliant with the Manitoba building code.
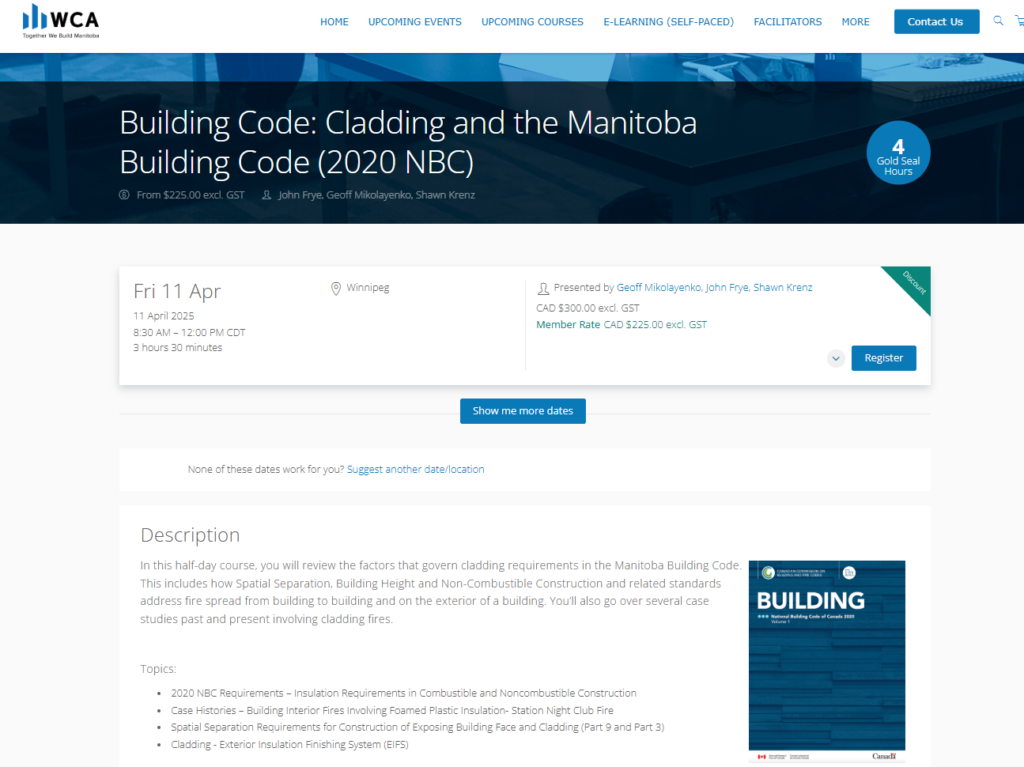
Clearly Communicate Rules and Risks: Effective compliance training must thoroughly explain the relevant laws, regulations, industry standards, and internal policies applicable to employees’ roles.
It should also clarify the reasons behind these rules, and the potential consequences of non-compliance for both the individual and the organization.
Must be Relevant and Practical: Compliance training should connect compliance requirements directly to employees specific job functions and daily tasks.
You can do this through using real-world examples, case studies, and practical scenarios, which helps employees understand how to apply compliance principles correctly in situations they might encounter.
Promote Positive Behavior: The training should be designed to be engaging and promote genuine understanding of the topic they are learning about.
Compliance training should reinforce ethical behavior and integrity, contributing to a workplace where compliance is seen as a shared responsibility, integrated into everyday decision-making.
Strong Compliance Training Programs Typically Includes These Key Components:
Overview of applicable laws and regulations: Detailed modules covering specific legislation relevant to the industry and employee roles.
Company code of conduct and ethics policy review: A thorough explanation of an organizations core values, ethical standards, and ethical behaviors.
Specific policy deep dives: Focused training on critical internal policies such as anti-bribery, and corruption, conflicts of interest, information security and acceptable use, gifts and entertainment, and expense reporting.
Read More: 12 Best Compliance Training Software & LMS Platforms
3. Technical Training
Technical training is a structured approach focused on equipping employees with the specific skills and knowledge required to perform their roles effectively, particularly concerning tools, technology, systems, and processes.
It is crucial to address the technical aspects of specific job roles to ensure that employees can navigate and manage the practical, job-related abilities required to perform tasks effectively.
All forms of technical training are usually highly specialized and directly applicable to the job in question.
Effective technical training should bridge the gap between a learner’s theoretical understanding and their hands-on ability to operate equipment, use software or execute technical procedures.
Technical Training Program Example
The example below, is from another Arlo customer, All Borough Safety Council, who offer technical training skills to construction companies, and employees in the New York area.

Effective Technical Training Programs Should:
Align with Job Requirements: Directly address the specific technical skills, and knowledge employees need to perform their current roles successfully.
Have Hands-on Application: Provide opportunities for learners to practice using the tools, software. Or equipment in a realistic or simulated environment.
Subject Matter Expertise: The training should be delivered by trainers or mentors who have deep knowledge and practical experience in the specific technical area.
The Key Components of a Technical Training Program Often Include:
Foundational Concepts and Theory: Explanations of the underlying principles, architecture, terminology and core concepts related to the specific technology, software, hardware or process being taught.
Hands-on labs and exercises: Dedicated time and environments (like sandboxes or simulators) where learners can actively practice using the tools, writing code, configuring systems, or operating equipment.
Explanations of the underlying principles, architecture, terminology, and core concepts related to the specific technology, software, hardware, or process being taught.
Instructor-led demonstrations and walkthroughs: Sessions led by Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) demonstrating how to perform key tasks, navigate interfaces, and apply technical concepts effectively.
4. Soft Skills Training
Soft skills training focuses on developing interpersonal attributes and communication abilities for employees to interact effectively in the workplace.
Skills that are encompassed in this type of training include communication, teamwork, problem-solving, adapting to new situations, and emotional intelligence. By focusing on these areas, organizations can create rich learning opportunities that empower employees to grow.
These skills are transferable across different roles, and industries and are really the foundation of strong relationships in the workplace, and a positive working environments.
Soft Skills Training Program Example
The example below of soft skills training is from Arlo customer Communispond, a communication skills training company, who offer a variety of programs for businesses and individuals. Similar to the customer service training example we mentioned earlier, many businesses look to external specialists to help their staff with soft skills training.
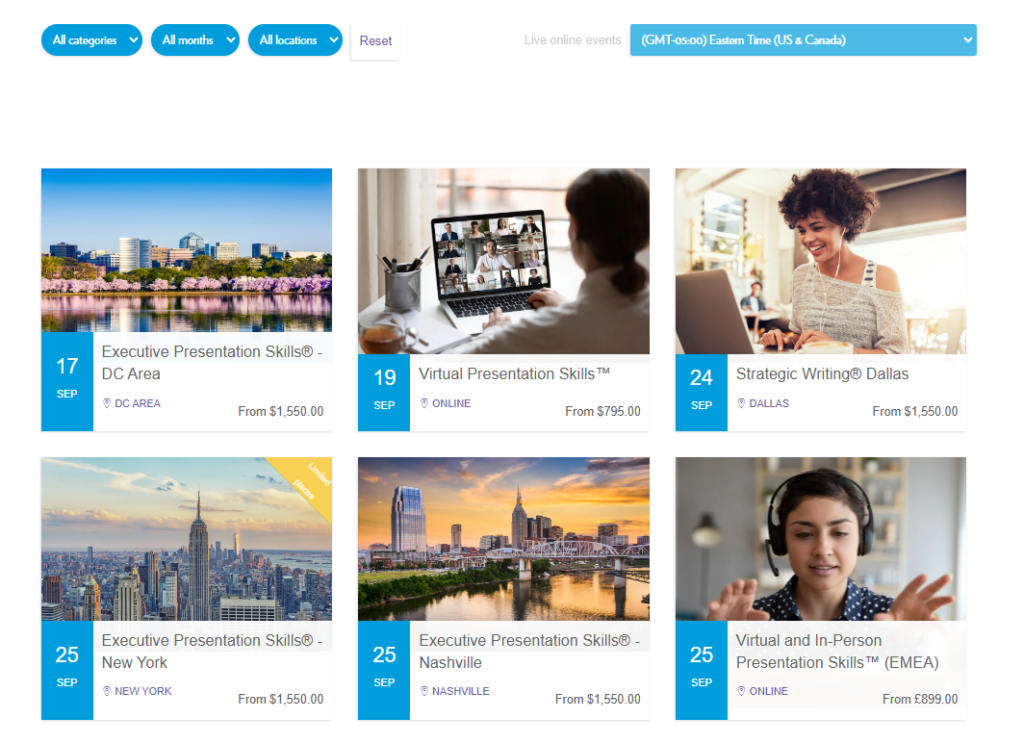
Effective Soft Skills Training Should:
Focus on behavioral change: soft skills training should focus on achieving an observable change in how employees act and interact. This can be done through practical exercises, role-playing, and simulations.
For example, if you were running a session on improving employees active listening skills, the instead of just discussing “active listening”, training should include activities where participants practice listening and summarizing a colleagues points, receiving feedback on their non-verbal cues and clarifying questions.
Include experiential learning: should incorporate activities like role-playing, simulations, group discussions and case studies to allow learners to practice skills in safe interactive environment’s.
Have a focus on self-awareness: Soft-skills training should help individuals understand their own communication style, behaviors, and emotional triggers to better manage workplace interactions.
Okay, here are three core components that encapsulate a soft skills training program:
Key Components of a Soft Skills Training Program Often Include:
Self-Awareness Building and Conceptual Understanding: Using self-assessments, reflection exercises, and focused instruction to help participants understand their own behavioral styles, and grasp the core principles and techniques of key soft skills (like communication skills or teamwork)
Constructive Feedback and Actionable Planning: Provide structured feedback on participants performance during practice activities, combined with guided planning to help them specific ways to apply their newly developed skills in the workplace.
5. Leadership Training
Leadership training is a structured process designed to develop and improve the capabilities of individuals to effectively, guide, motivate and direct teams and organizations.
Developing future leaders through these programs not only prepares them to inspire and manage teams but also secures the organization’s future by filling leadership gaps effectively.
LT programs tend to focus on helping employees cultivate a range of skills, behaviors and mindsets necessary for individuals to excel in leadership roles e.g. managerial positions, exec positions, or as an aspiring leader in an organization.
Effective leadership training helps companies develop their own talent pipeline, and achieve overall organization wide success.
Leadership Training Program Example
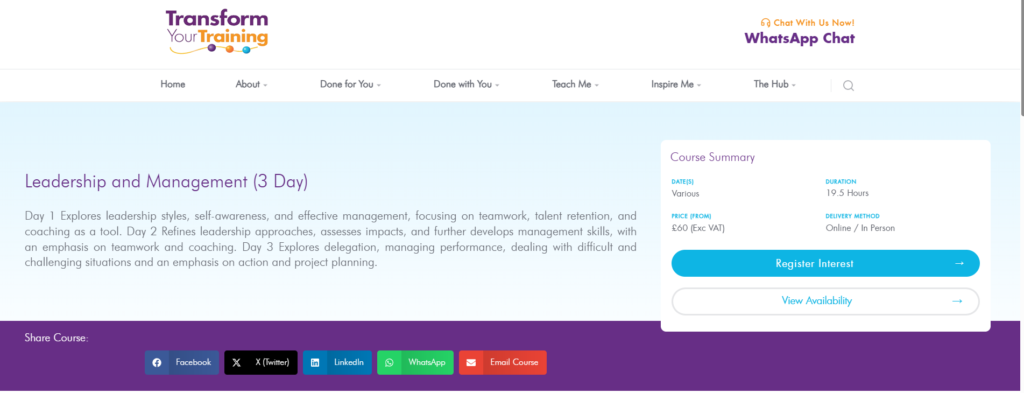
Effective Leadership Training Should:
Align with organizational strategy: LT should link leadership competencies directly to the companies goals, values, and future direction.
For example, if the organization has specific leadership skills gaps at different levels, e.g. they need more staff capable of becoming mid-managers, then the training content should be tailored with this goal in mind.
Blend theory and practice: Like all good training LT should combine foundational leadership concepts and frameworks with practical application.
Provide opportunities for self-reflection and assessment: LT should encourage leaders to understand their own leadership style, strengths, weaknesses, and impact on others through assessments, feedback, and guided reflection.
Provide mentoring and coaching: LT should include support mechanisms like one-one one coaching, or mentoring for individuals from more experienced leaders.
A Strong Leadership Training Program Typically Includes These Key Components:
Leadership Assessment and Self-Awareness: Using tools like 360-degree feedback, leadership style inventories, and guided self-reflection to help participants understand their current leadership strengths, weaknesses, impact on others and areas for development.
Core Leadership Competency Modules: Focused instruction on essential leadership skills such as strategic thinking and planning, vision setting, effective decision making, financial acumen (understanding budgets, P&Ls) and more.
People Management and Team Development Skills: Training on crucial interpersonal aspects of leadership, including motivating and engaging employees, effective communication (one-on-one, group, public speaking), delegation, performance management (setting goals, providing feedback, coaching), conflict resolution, and building high-performing, inclusive teams.
6. Onboarding Training
Onboarding training is the process of integrating new employees into an organization and their specific roles.
It involves providing essential information on company policies and culture, delivering necessary job-specific knowledge and skills training.
The goal is to quickly enable new starters to become productive and contributing members to an organization.
Effective Onboarding Training Training Should:
Start before-day one (pre-onboarding): It should initiate the process from the moment a candidate accepts an offer, including providing necessary information, completing initial paperwork. For example, sending a welcome email with details about their first day, company values, code of conduct, procedures and benefits.
Onboarding training introduces new employees to the company culture, expectations, and daily operations. It lays the foundation for employee morale and retention by setting clear expectations and building early confidence.
Structured and Organized: Provides a clear roadmap for the new employee’s first days, weeks, and months, outlining key activities, training modules, and introductions.
Sets Clear Expectations: Clearly communicates job responsibilities, performance standards, goals, and how their role contributes to the larger organizational objectives.
Key Components of an Onboarding Training Program Often Include:
Pre-boarding activities: As mentioned above pre-boarding materials such as info on setting up necessary system access, compiling initial HR paperwork before the employees first day.
Company culture and values immersion: Introducing the organizations mission, vision, values, and key policies to employees.
Role-Specific Training and Expectations: Detailed clarification of the jobs responsibilities, performance expectations, key performance indicators, and training on the specific tools, software and processes required for the role.
Onboarding Training Program Example
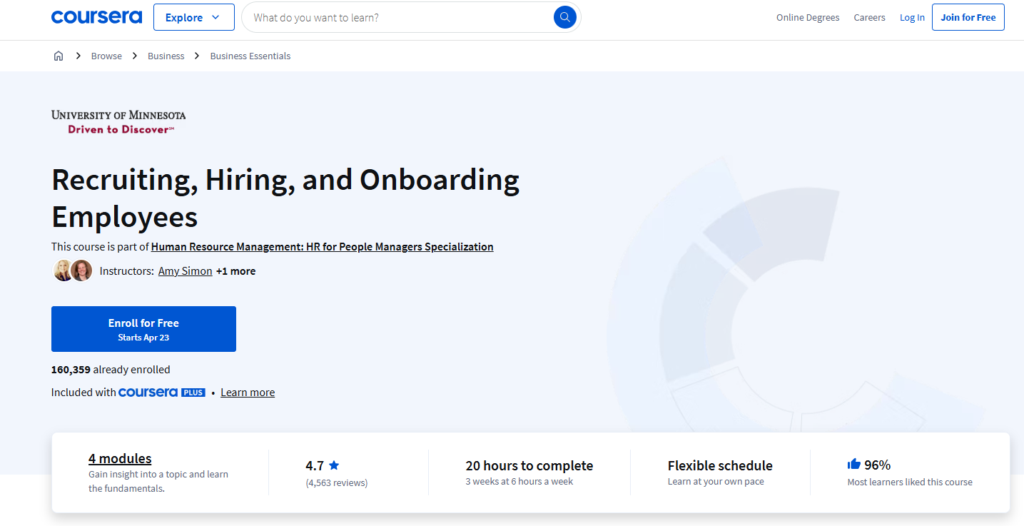
It was tricky to track down an onboarding training example, as each program is independent to each company.
So, for this example we’ve featured a course offered by the University of Minnesota, hosted on Coursera: Recruiting, Hiring, and Onboarding Employees, a well rated course to check out if you’re looking to improve your company’s onboarding processes.
7. Product Training
Product training is specifically designed to educate employees about the features, benefits, functionality and applications of a company’s products or services.
The training should ensure that employees, particularly those in sales and marketing, and customer support have the in-depth knowledge required to effectively discuss, demo and support the product the company is selling.
Product knowledge training is essential for employees in customer-facing roles, as it equips them with a thorough understanding of the products, boosting their confidence and enhancing conversion rates during sales pitches.
The goal is to build product expertise and confidence across relevant teams.
Product Training Program Example
The example below is a sample course we’ve created using Arlo’s elearning authoring tool on how to use Arlo’s course templates.
With the tool, you can upload documentation about your product and transform the document into an interactive elearning course, or design your own course from scratch.
Effective Product Training Should:
Focus on ‘Why’ and ‘How’: Go beyond listing features by explaining the product’s value proposition, how it solves customer problems, and demonstrating practical usage.
For example, instead of simply stating that software has a reporting function, show how to generate specific reports and explain what business questions those reports help answer.
Tailored to audience needs: Content and depth vary based on the employee’s role and their level of interaction with the product and customers. For example, training for a sales team will differ from training for a support team or engineering.
Includes Hands-on Experience: Provides opportunities for employees to interact directly with the product, practice using its features, and troubleshoot common issues.
Covers Competitive Landscape: Educates employees on how the product compares to competitors’ offerings, highlighting key differentiators and advantages.
Key Components of a Product Training Program Often Include:
Deep dive into product features and functionality: comprehensive exploration of what the product or service does, how its specific features work, available configurations, and relevant tech specs.
Understanding the products value prop and customer benefits: Product training should clearly articulate the core problems the product solves, the specific benefits it delivers to users/customers, and its unique selling points.
Target audience and use case analysis: Defining the ideal customer profiles, understanding their needs and pain points, and getting clear on the primary and secondary ways the products is sued to meet those needs.
8. Sales Training
Sales training is a targeted learning process designed to equip individuals and teams with the knowledge, skills, and techniques necessary to effectively sell products or services, manage customer relationships, and achieve revenue goals.
It focuses on getting an individual to understand and improve selling behaviors, understand customer needs, navigating sales processes and objections and using sales tools. Sales training helps employees learn new skills and improve their selling behaviors, leading to a more engaged and motivated workforce.
The aim is to improve sales performance, increase conversion rates, and drive business growth.
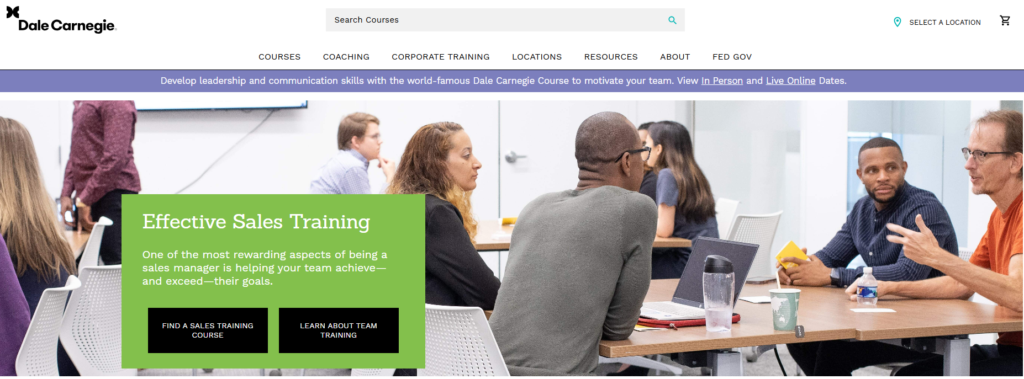
Sales Training Program Example
The example here is another from Dale Carnegie Training. For areas like sales, for training to really be effective it really needs to be customized, and tailored to your company.
What works in one industry, may not in another, and there are many different ways to sell a product which can be successful.
Key aspects that make this training effective:
Focus on Practical Application: Use realistic scenarios, role-playing, and simulations to let salespeople practice techniques in a safe environment before engaging with real customers—for example, running mock sales calls based on common objections or various buyer personas.
Tailored to the Sales Process and Methodology: Aligns training content with the company’s specific sales stages, strategies, and tools used by the sales team.
Includes Product and Market Knowledge: Provides in-depth understanding of the products/services being sold, their value proposition, the target market, and the competitive landscape.
Develops Core Sales Skills: Covers essential skills such as prospecting, lead qualification, communication, active listening, negotiation, objection handling, and closing techniques.
Key components of sales training programs often include:
Sales Process and Methodology Training: Detailed walkthrough of the company’s specific sales stages, reinforcement of the adopted sales methodology, and effective CRM management.
Core Selling Skills Development: Focused training and practice on essential selling skills, e.g. prospecting and lead gen, lead qualification and needs analysis, active listening and effective questioning and more.
9. Diversity and Inclusion Training
Diversity and Inclusion (D&I) training is designed to educate employees on the value of individual differences, and create a workplace where everyone feels welcomed, respected, and psychologically safe to contribute.
This training fosters a culture of continuous learning within organizations, enhancing employee retention and bridging skill gaps.
The training provides practical guidance on how to create an equitable workplace, and typically covers topics such as identifying and addressing personal biases, and understanding how to work effectively with colleagues from varied backgrounds.
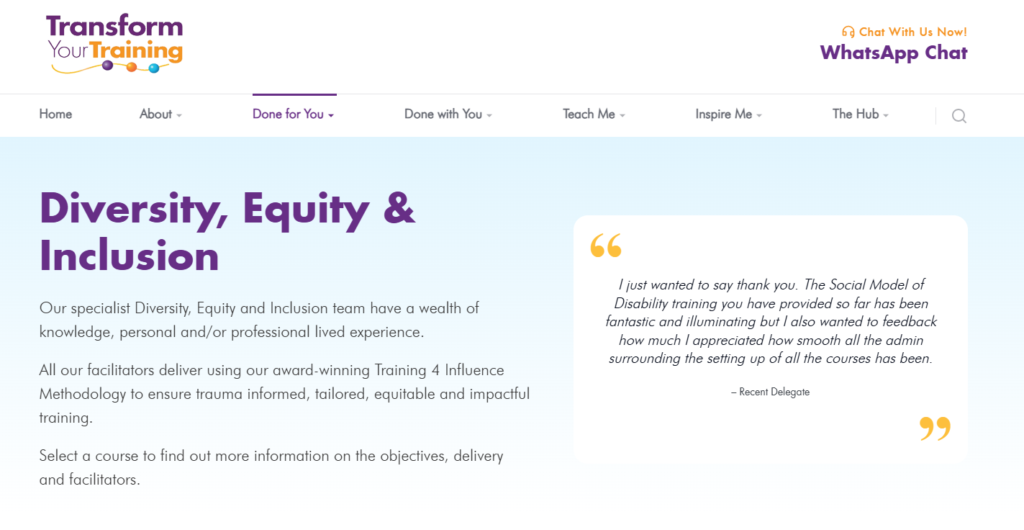
Diversity and Inclusion Training Example
This example is from Arlo customer Transform Your Training, who deliver a wide range of DE&I courses to company’s to help them develop a more equitable workplace.
Effective D&I training should:
Needs Assessment Tied to Behavior: Identify specific D&I-related behaviors or incidents within the organization that need to change, rather than just general awareness gaps.
For example, conducting focused interviews with different cross-functional teams to understand specific communication challenges or instances where diverse perspectives are not being fully leveraged in meetings or projects.
Scenario-Based and Experiential Learning: Design activities that allow employees to practice applying inclusive behaviors in simulated workplace situations. For example, using branching scenarios in e-learning or facilitated role-playing workshops where participants navigate conversations involving differing perspectives or potential biases.
Focus on Skill-Building, Not Just Awareness: Dedicate significant training time to developing practical skills like active listening across differences, providing inclusive feedback, and intervening constructively in non-inclusive situations.
E.g. delivering modules with specific techniques for addressing biased language or making sure of equitable participation in meetings, followed by practice exercises.
Key components of Diversity and Inclusion Training often include:
Foundational concepts: Clear definitions of core terms like Diversity, Equity, Inclusion and Belonging.
Unconscious bias awareness and mitigation: Educating participants on what unconscious bias or implicit bias is ,how it forms, common types and its impact on workplace decisions.
Cultural competence and sensitivity: Developing awareness, knowledge and skills to interact respectfully and effectively with people from diverse cultural backgrounds, values and communication styles.
10. Safety Training
Safety training provides employees with the essential knowledge and skills to perform their jobs safely, identify potential hazards, and respond correctly in emergency situations.
Safety training also addresses skill gaps in employee competencies related to safety procedures, ensuring that all staff are adequately prepared to handle potential risks.
The training is mandatory in many industries, and roles to minimize workplace risk, and ensure compliance with regulations and laws.
The focus for safety training is on practical procedures, and awareness to maintain a secure working environment for all personnel.
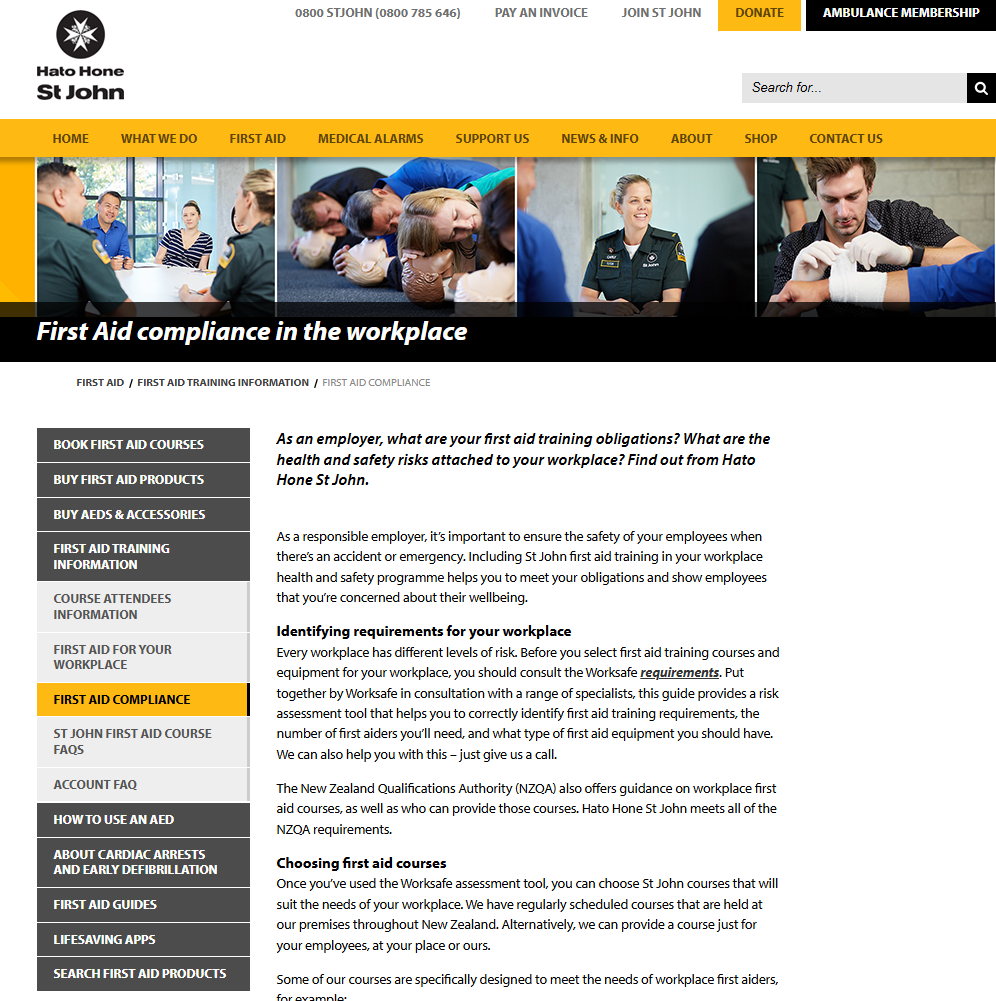
Safety Training Program Example
This example is from Halo Hone St John, who offer first aid compliance, and first aid skills training programs to businesses.
Effective safety training should:
Have Specific Hazard Identification to Role/Environment: Training content should be tailored to the actual hazards employees will encounter in their specific job functions and work locations.
For example, for manufacturing staff, include visual examples and procedures for operating specific machinery safely; for office workers, focus on ergonomics and emergency evacuation routes.
Promote Hands-on Practice with Equipment/Procedures: Practical exercises should be included for using safety equipment, performing emergency procedures, or demonstrating safe techniques for tasks relevant to the job.
Be Regular and Updated Frequently: Implement a schedule for recurring training to reinforce safety knowledge and update employees on changes to procedures, regulations, or workplace hazards.
11. Cybersecurity Training
Cybersecurity training in the workplace focuses on educating employees about potential digital threats, company security policies, and safe online practices to protect organizational data and systems.
The training provides skills and knowledge to recognize and respond to common cyber risks such as phishing or malware. The goal is to reduce human error, which is a significant factor in security breaches, and build a security-aware workforce.
Cybersecurity Training Program Example
The example below is from the Employers and Manufacturers Association (EMA) who offer a wide variety of training courses, including cybersecurity training to businesses across New Zealand.
Effective cybersecurity training should:
Contain Risk and Role-Based Content: Training modules should be relevant to address the specific roles and departments within an organization.
For example, finance teams may require specific training on wire transfer fraud and secure transaction processes, while IT personnel require more in-depth training on network security protocols.
Contain Simulation and Practical Exercises: Training should Incorporate realistic simulations, such as phishing email tests or simulated malware attacks to allow employees to practice identifying and responding to threats.
One example could be sending out simulated phishing emails and tracking click rates, followed by targeted training based on the results.
Focus on Recognizable Threats: Concentrate training on the most common and impactful cyber threats employees are likely to encounter daily.
12. Time Management Training
Time management training provides employees with techniques and strategies to plan, organize, and control their time spent on specific activities to increase efficiency and effectiveness. This type of training keeps employees motivated by helping them manage their time and workload effectively.
It equips individuals with practical methods for prioritizing tasks, scheduling work, setting goals, and minimizing time spent on non-essential items. The training aims to improve individual productivity and help them better manage their time and workload.
Time Management Training Program Example
This example is a course offered by the American Management Association, who train business professionals across the USA on topics like time management, and other professional development topics.
Effective time management training should:
Focus on Practical Application and Tools: Provide employees with specific, actionable techniques, and digital or physical tools they can immediately apply to their daily workflow. Such as tips on auditing their time, and analyzing the results.
Address Real, Identified Workplace Time Challenges: Directly target the actual time management difficulties employees in the organization experience, using insights from needs assessments like analyzing common pain points revealed in workflow discussions or time audits.
Support Ongoing Habit Building and Reinforcement: Include resources and follow-up methods to help employees consistently apply learned techniques over time, like providing digital templates for daily planning or suggesting peer accountability check-ins.
13. Quality Assurance Training
Quality Assurance (QA) training focuses on educating employees about the processes, standards, and procedures used to ensure products or services consistently meet defined quality requirements and customer expectations. Innovative methods can be used to enhance learning and engagement in Quality Assurance training.
It generally covers methodologies for preventing defects and improving processes throughout the development or delivery lifecycle, with the goal of giving employees the practical skills and mindsights to maintain high standards of output.
Quality Assurance Training Program Example
This is another example hosted on Coursera. A clinical trials data management and quality assurance course by John Hopkins University.
Effective quality assurance training should:
Teach Foundational Quality Principles: Provide employees with a core understanding of quality management concepts and relevant organizational or industry standards, such as explaining why consistent procedures are critical for quality outcomes.
You should also show employees where to access standard operating procedures (SOPs) or quality guidelines relevant to their roles.
Focus on Application: QA training should equip employees with the skills to use the actual tools, and follow the procedures involved in the orgs QA activities. Such as, providing hands-on training and using specific inspection equipment, or completing digital quality checklist forms accurately,
14. Conflict Resolution Training
Conflict resolution training teaches employees approaches and communication techniques to constructively address and resolve disagreements within the workplace. This type of training fosters relationship building by promoting effective communication and collaboration.
This type of training provides skills for understanding conflict dynamics, helps employees manage emotional responses, and find mutually acceptable solutions.
Training of this nature should aim to reduce negative interactions, and support the maintenance of professional relationships.
Conflict Resolution Training Example
This example brings an interesting twist! Arlo customer Safety ‘N’ Action, New Zealand’s leading provider of Health and Safety training and advisory services, offers conflict de-escalation training in a VR setting.
Having the training in a VR setting, moves the learner from taking a back seat to learning and propels them to be a leading role in the story.
A VR setting helps the company offer up scenarios that mimic real-life experience, and better equip team members with the skills to look for cues and de-escalate potential high risk situations.

Effective Conflict Resolution Training should:
Teach Core Communication and De-escalation Skills: Equip employees with fundamental techniques for navigating tense conversations, such as practicing active listening to understand perspectives fully, or learning phrases and approaches to de-escalate emotional situations.
Provide Structured Frameworks for Conflict Resolution: Introduce clear step-by-step models or processes that employees can follow to address conflicts systematically, including stages like identifying the core issue, exploring interests and brainstorming solutions.
Provide Opportunities for Practice: The training should provide opportunities for learners to apply learned skills in simulated workplace conflict situations, through role-play exercises or case studies. So that they can learn and get constructive feedback.
15. Upskilling
Upskilling involves teaching employees new skills, or improving existing skills within their current job function to improve performance and adapt to changing job requirements. Upskilling also contributes to career development by providing employees with opportunities to enhance their skills and advance within their organizations.
It involved providing targeted learning opportunities that build upon an employees existing expertise.
The goal is to increase an individuals capability and value in their current role.
Upskilling Training Program Example
For this example, we thought we’d show more of a fully fledged company wide internal training program
Amazon’s Upskilling 2025 Initiative is a $1.2 billion investment designed to help employees gain crucial skills for higher-paying, in-demand roles, whether technical or non-technical. The initiative is tailored to help workers to adapt to evolving industry standards and ensure their long-term career growth.
For example, Amazon Technical Academy offers training for employees in non-technical positions, equipping them with the skills needed for roles in software engineering. The program combines instructor-led sessions and project-based learning.
Additionally, AWS Training and Certification is a skill development program aimed at all employees, regardless of their current role, to help them become proficient in working with AWS cloud technologies.
Effective Upskilling Training should:
Target Skills Directly Relevant to the Employee’s Current Role and Future Evolution: Identify specific competencies needed to excel in the employee’s present position and anticipated changes, such as providing a marketing specialist with advanced training on new digital analytics tools the team is adopting or enhancing a software developer’s skills in a newly used programming language.
Offer Flexible and Accessible Learning Formats: Provide training through various modalities that accommodate employees’ existing workloads and learning preferences, like offering bite-sized e-learning modules employees can complete around their tasks or providing access to on-demand video tutorials for new software features.
Include Opportunities for Applying New Skills on the Job: Design learning experiences that allow employees to practice and integrate newly acquired skills into their daily tasks, such as assigning small projects where employees can use the new techniques or setting up peer coaching sessions for practicing updated processes.
16. Reskilling
Reskilling is a training initiative designed to teach employees new skills or prepare them for a different role within an organization. It involves a more comprehensive learning program than upskilling, focused on transitioning employees to new functions.
The goal of reskilling is to help a company retain valuable talent by equipping them for different opportunities within the company.
Example of a Reskilling Program
In 2018, AT&T launched a massive reskilling program for almost half its workforce, after discovering that 250,000 employees lacked the necessary skills needed to keep the company competitive.

Effective Reskilling Training should:
Clearly Define Target Roles and Required Skill Sets: Identify the specific jobs employees are being reskilled for and thoroughly outline the new technical and soft skills they’ll need for success.
Provide Comprehensive and Structured Learning Pathways: Offer a clear, step-by-step training program that builds foundational knowledge and skills progressively for the new role, including a combination of formal instruction, hands-on practice, and potentially mentorship, like designing a multi-month program with classroom training, simulations, and on-the-job shadowing in the target department.
Include Support Mechanisms for the Transitioning Employee: Provide guidance, coaching, and resources to help employees navigate the change to a new role, addressing potential anxieties and supporting their integration into a new team.
17. Cross-Training
Cross-Training involves teaching employees skills and knowledge to perform tasks outside their primary job responsibilities, often within the same team or department.
It focuses on building versatility, and redundancy in skills across a group. Cross-training incorporates diverse learning activities to enhance learning and engagement.
The goal is to increase team flexibility, improve collaboration, and ensure continuity of operations when individuals are absent or workloads shifts.
Example of a Cross Training Program
A well-known example of a cross-skilling employee training program is Google’s Career Certificates Program. Google developed the program to offer employees and job seekers the opportunity to cross-skill into new, high-demand areas.

Effective Cross-Training should:
Identify Critical Skills and Tasks for Coverage: Determine which specific job duties or processes are essential for team function and need to be performed by multiple members, such as analyzing workflows to identify bottlenecks or tasks performed by only one person that would cause problems if they were absent.
Pair Experiential Learning with Clear Documentation: Combine hands-on practice or job shadowing with access to clear, step-by date standard operating procedures (SOPs) or guides or the tasks being learned, like having an employee shadow a colleague performing a specific technical process while following along with a detailed checklist or reference document.
Implement a Structured Plan for Knowledge Transfer and Practice: Establish a clear schedule and method for employees to learn and practice the secondary tasks, including dedicated time for training and opportunities for supervised execution of the new duties, such as setting aside specific hours each week for cross-training activities and scheduling supervised sessions for key tasks.
Tips for Creating an Effective Employee Training Program
1. Use the most appropriate delivery method
As you can see from many of the example we’ve included, there’s no one size fits all delivery method that works best for employee training, so you’ll want to make sure you have a process in place for determining an appropriate method.
You can do this by thinking about what types of skills employees need to gain from the training program. For example, if its a safety training program, in-person expert instruction will be needed. Often though, a program will be made up of various delivery methods: in-person, virtual and blended training.
In our Ultimate Guide to Instructor-Led Training, training expert, and Arlo customer Tammy Banks, gave a great example of this, with a client she recently worked with:
“We recently worked with a physiotherapy company that has offices all over the country. They have managers for all their offices, and they also have clinical leads. And they wanted to enroll all of them in our leadership training program.
So, to effectively deliver the program we decided to completely tailor the structure of the course to their needs. Everyone comes together face to face in London for a full day, and then after they have fortnightly 90 minute live online sessions.
Alongside the live sessions delegates have their own elearning modules to work through, and the elearning modules directly feed into what they’re going to learn in the live sessions. The facilitator has access to a portal where they can see how each delegate is progressing through the self-paced modules.
Delegates are also part of an online community where they can discuss what they’re learning with one another and collaborate. We then have another face to face session at the end of the course to celebrate everyone completing the course”.
2. Use the Right Tools to Scale Training
To effectively deliver employee training you need the right software in place. Platforms that can accomplish this fall into the categories of Learning Management Software, and Training Management Software.
To create elearning, look for a platform with an LMS or TMS with an integrated elearning authoring tool. This piece of software allows you to design, develop, and deploy interactive learning content—such as quizzes, videos, simulations, and modules—directly within the training platform.
3. Use Instructors with Real-World Experience
“When an operational expert delivers a session, they bring more than just experiences and examples to the table. They also bring a true understanding of the sector, the customer group, and how to facilitate the learning objectives in a way that will influence a delegate’s daily work.”
These are the words again of Tammy Banks, and its a point that cant be overemphasized. Any employee training you run should be delivered by a knowledgeable, engaging instructor. Tammy uses the following set of criteria to determine an ‘expert instructor’, which you can use to guide your own selection:
- Undertaking a similar role to the delegates, either voluntarily or in a paid capacity
- Working in a connected field
- Working with the customer group
- Having real-life experience with the customer group
- Having personal connections with the customer group.
4. Measure Results and Improve Continuously
You can’t improve what you don’t track. It’s important to track surface-level metrics like attendance and completion rates. But you also needs ways to measure performance after the training has taken place.
Some tips on doing this include:
- Identify relevant KPIs e.g. performance data, time and money savings, increased sales revenue – whichever is most relevant to the training program
- Pre- and Post-Training Assessments: Measure knowledge gains by testing before and after the training.
- Follow-Up Surveys: Ask participants how useful the training was and if they feel confident applying what they learned.
- Behavioral Observations: Check in with employees to see if they’re using their new skills on the job.
- Track Long-Term Impact: Revisit KPIs months later to see if the training led to lasting changes like higher sales or productivity.
Deliver Effective Employee Training with the #1 Training Platform
Of course, to deliver effective employee training you need a platform to help. Arlo is an all-in-one training platform with features to create, schedule and deliver in-person, virtual, blended and elearning training.
If you want to try these features for yourself, you can get started with a 14-day free trial below 👇
Get your time back, increase training revenue, and deliver better training with Arlo. Start a free 14-day trial today.
FAQs
Employee training plays a key role in improving performance by developing the skills employees need to do their jobs effectively. Well-structured and implemented workplace training programs lead to increased productivity, stronger performance, greater job satisfaction, and a stronger bottom line.
Like we mentioned earlier, successful employee training programs often combine a variety of training methods, primarily instructor-led training, virtual, and self paced learning. A variety of methods helps support different learning styles, and help reinforce key skills.
Start by identifying your teams specific needs and goals. There’s obviously a tonne of different employee training programs that you might need to run. So start with the goal in mind, and this will start to lead you to the type of course you need to prioritize.